|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Fotografii | Monede | Timbre | Schite | Cautare |
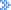 Frank Plumpton Ramsey
Frank Plumpton Ramsey




Ramsey entered Winchester College in 1915 and from there he won a scholarship to Trinity College, Cambridge. He completed his secondary school education at Winchester in 1920 and he entered Trinity College, Cambridge, to study mathematics. At Cambridge, Ramsey became a senior scholar in 1921 and graduated as a Wrangler in the Mathematical Tripos of 1923. After graduating, Ramsey went to Vienna for a short while, returning to Cambridge where he was elected a fellow of King's College Cambridge in 1924. It is worth noting that this was a most unusual occurrence, and in fact Ramsey was only the second person ever to be elected to a fellowship at King's College, not having previously studied at King's. In 1925 Ramsey married Lettice C Baker and they had two daughters. In 1926 he was appointed as a university lecturer in mathematics and he later became a Director of Studies in Mathematics at King's College. It was a short career, for sadly Ramsey died at the beginning of 1930. However, in the short time during which he lectured at Cambridge he had already established himself as an outstanding lecturer. Broadbent writes in :
Although Ramsey was a lecturer in mathematics, he produced work in a remarkable range of topics over a short period. As well as starting up the new area of mathematics now called 'Ramsey theory', which we say more about below, he wrote on the foundations of mathematics, economics and philosophy. He published his first major work The Foundations of Mathematics in 1925. In this work he accepted the claim by Russell and Whitehead made in the Principia Mathematica that mathematics is a part of logic. Ramsey's aim in this paper, however, was to improve on the Principia Mathematica and he did so in two ways. Firstly he proposed dropping the axiom of reducibility which, he writes, is:
His second simplification is to suggest simplifying Russell 's theory of types by regarding certain semantic paradoxes as linguistic. He accepted Russell 's solution to remove the logical paradoxes of set theory arising from, for example, "the set of all sets which are not members of themselves". However, the semantic paradoxes such as "this is a lie" are, Ramsey claims, quite different and depend on the meaning of the word "lie". These he removed with his reinterpretation that removed the axiom of reducibility. Ramsey published Mathematical Logic in the Mathematical Gazette in 1926. In this he attacks the:
for denying that propositions are either true of false. He writes:
He also criticises Hilbert in Mathematical Logic saying that he had attempted to reduce mathematics to:
His second paper on mathematics On a problem of formal logic was read to the London Mathematical Society on 13 December 1928 and published in the Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society in 1930. This examines methods for determining the consistency of a logical formula and it includes some theorems on combinatorics which have led to the study of a whole new area of mathematics called Ramsey theory. Harary describes this birth of Ramsey theory in where he writes the following:
The combinatorics was introduced by Ramsey to solve a special case of the decision problem for the first-order predicate calculus. However, as Mellor points out in , it is now known that there is a more direct proof than that given by Ramsey, while the general case of the decision problem cannot be solved. So Mellor points out that :
Ramsey made a systematic attempt to base the mathematical theory of probability on the notion of partial belief. This work on probability, and also important work on economics, came about mainly because Ramsey was a close friend of Keynes . Being a friend of Keynes certainly did not stop Ramsey attacking Keynes ' work, however, and in Truth and probability , which Ramsey published in 1926, he argues against Keynes ' ideas of an a priori inductive logic. Ramsey's arguments convinced Keynes who then abandoned his own ideas. Ramsey, proposing a probability measure based on strength of belief, :
In economics, Ramsey wrote two papers A contribution to the theory of taxation and A mathematical theory of saving. These would lead to important new areas in the subject. It was philosophy, however, that was Ramsey's real love. He wrote a number of works such as Universals (1925), Facts and propositions (1927), Universals of law an of fact (1928), Knowledge (1929), Theories (1929), and General propositions and causality (1929). Braithwaite writes in :
One would have to say, however, that Ramsey's work in philosophy has been somewhat overshadowed by that of Wittgenstein . Recently, however, Ramsey's work in philosophy seems to be receiving more attention. Several of the articles cited in the references paint vivid pictures of Ramsey's character. For example Braithwaite writes in :
Mellor, in , paints a similar picture:
He was tall (six feet three inches) and bulky, short-sighted, wore steel-rimmed spectacles and appeared clumsy but was in fact a good tennis player. He produced his remarkable output in four hours a day - he found it too exacting to do more - in the mornings, with afternoons and evenings often spent walking or listening to records. He listened a lot to classical music, both live and recorded, and was a keen hill-walker. In his potential is emphasised:
Ramsey suffered an attack of jaundice and was taken to Guy's Hospital in London for an operation. He died following the operation.
Source:School of Mathematics and Statistics University of St Andrews, Scotland |